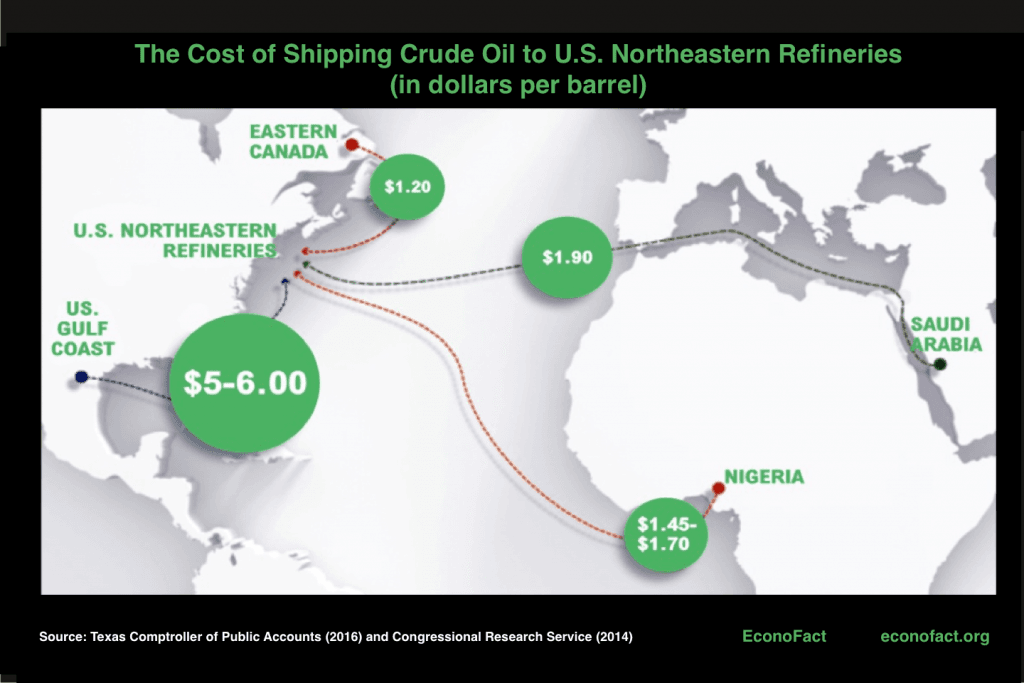
China is likely the largest economy in the world, 11% lager than the US calculated here based on food purchasing parity They also have a larger army and navy, 754 ships vs 440, with military ambitions for Taiwan and new, man-made islands in the China sea. They continue to add aircraft carriers and submarines (we’re still ahead there), but China fuels all this with oil. They use some 17 million barrels per day: 11.3 million imported by ship, and put another million bb//day per into reserve in case there is a shutoff.
A problem for China is that their internal production, 4.5million bbl/day, is far below their consumption, a big vulnerability. One of their main suppliers, Venezuela, just went off line, sending 800,000 bbl/day of oil to the US that would have gone to China. Two other of their major, sanctioned suppliers, Iran and Russia have had delivery issues too; a disruption in oil could cause a revolt in China. Perhaps this fear will drive China to war with us, similar to the way that a cut off in oil caused Japan went to go to war with us in WWII, see table below. Japan had the choice of war or shutting down their economy and ambitions. Perhaps China may choose the same if Iran and/or Russia goes off-line. That was my worry, I’m no longer that concerned.
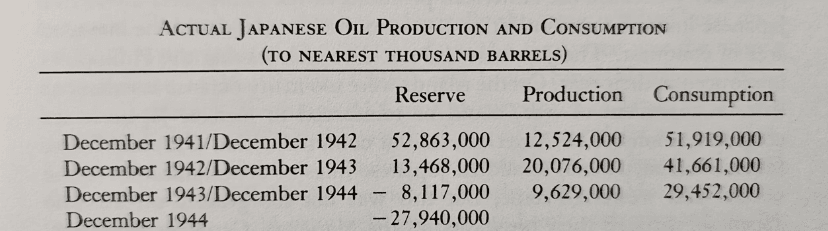
Currently, China buys most of its imported oil from four countries: Russia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and Iraq; two of these are under sanction. China used to get another 0.8 million barrels per day from Venezuela, another country under sanction, but that route was closed by Trump last week. Buying from sanctioned countries saves them significantly, and supports the BRICS alliance, an alliance specifically against the US (NAFTA?) and the EU. The money they pay to Russia and Iran supports the war against Ukraine, plus ISIS’, war against us, and the mullahs oppression in Iran.
China was buying, from Russia, some 2.2 million barrels of oil and refined products, plus natural gas and coal (China is a big coal user). The rest of Russia’s output goes to India, Turkey, and the EU. The EU buys more than half of eastern Russia’s natural gas output, shamefully it has likely kept Germany from collapsing. The problem for China is that Russian production is under attack from Ukraine. Ukraine sank or disabled several Russian tankers, and we took some more; they’ve blown up pumping stations, including three on the Caspian Sea, set fire, to a large liquid natural gas terminal and damaged the major off-load platform for Kazakh oil. According to the Foundation for Democracy report, here, by October 2025, China was down to getting only 800,000 bbl/day from Russia, a major blow, and Ukraine’s attacks continue.

Iran is another major supplier under attack. Up until recently they provided nearly 2 million barrels of oil per day, 90% of Iran’s seaborne export. Much of that went indirectly, going to Indonesia, turkey, Iraq, and Kuwait where it was relabeled, blended or refined to avoid sanction penalties. Everyone makes a profit here, but Iran is in the midst of a revolution. Last week, Trump imposed an across-the board 25% additional tariff on counties that help Iran avoid the sanctions. My guess is that this tariff will be effective and that it will last until the revolution is over. His tariffs have been effective and profitable, it seems.
China has non-sanctioned suppliers. They buy some 1.6 million barrels per day from Saudi Arabia, about 1.2 million bbl/day, from Iraq, about 1.3 million bbl per day from Malaysia, about 700,000/ day from Brazil, and about 900,000/day from the USA. In principle, they could make up any losses by buying more here, but the price would be higher. Worse yet, Trump could cut China off. That would be devastating; it’s the reason China built up a reserve of 2.2 billion barrels amounting to 6 months of current use. Japan did something similar in 1941, building up a year’s worth. They then used all of it in the first year of the war, while conquering Indonesia, a new supplier. For all I know, Trump’s activities in Venezuela and Iran are meant to force a war decision on China before they are strong enough to defeat us. It seems to have been FDR’s logic.
China’s main way to address a possible oil disruption, as best I can tell, has been to push EVs development. They’ve financed some 500 new EV companies who now (late 2025) provide about 50% of new Chinese automobiles. Another 19% are hybrids. In the US, only 8% of new cars are EVs, and 16% hybrids. Large-scale use of EVs lessens the pressure on Chinese leaders to find oil sources, some 40% of oil imports can be assumed to go to fuel automobiles; if China were to go 80% EV, it would save 5.5 million barrels/day, more than it gets from Russia and Iran combined. For now, though, China has a big need for gasoline, and has a big excess in EV manufacturing. It has turned to Canada both as a customer for EVs and as a supplier for oil.
Last week, Canadian PM, Mark Carney visited China and announced a “Strategic Partnership” on Agriculture, energy, finance, and Global governance.” There’s no specific mention of oil, but it’s implied. China gets most favored nation status sending goods, including EVs to Canada at rates lower than on US goods. China will export some 50,000 EVs in 2026, rising to 70,000 by 2030 with tariffs set to 6.1%. US-made cars are tariffed at 25%. Canadians will get visa-free, tourist visits), plus a loan of $1B to be used buying Chinese ships. In Davos last week, “We are in the midst of a Rupture” away from the US. He urged the EU and other “middle powers” to band together. He talks like China is a good, reliable friend to Canada, and like the US isn’t. I would worry more about his comments and the “global governance” phrase, if the EU seemed to be going along, but it is not. Nor do I see a real move in China for war. I see positive effects of increased EV sales for China, Canada, and the world. Even if the quality isn’t great, Go Canada, go peace.
Robert Buxbaum, January 25, 2026. *The plan to attack Pearl Harbor was made in December 1940, a year before it happened and 9 months before we cut off oil shipments. We cut off oil shipments in September, following Japan’s invasion of Indonesia, done to take the oil there. While oil was not Japan’s only aim in WWII, it was an aim and a big participant at every step.