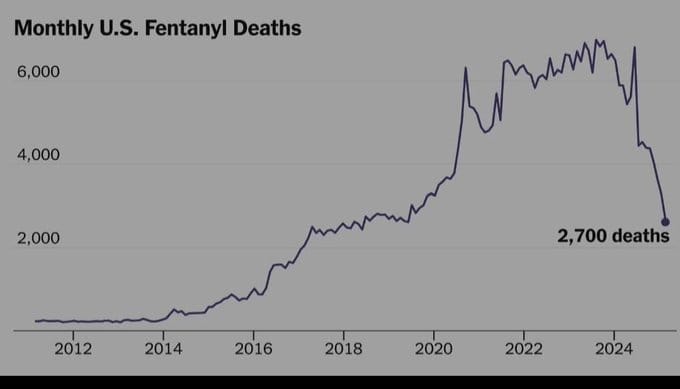
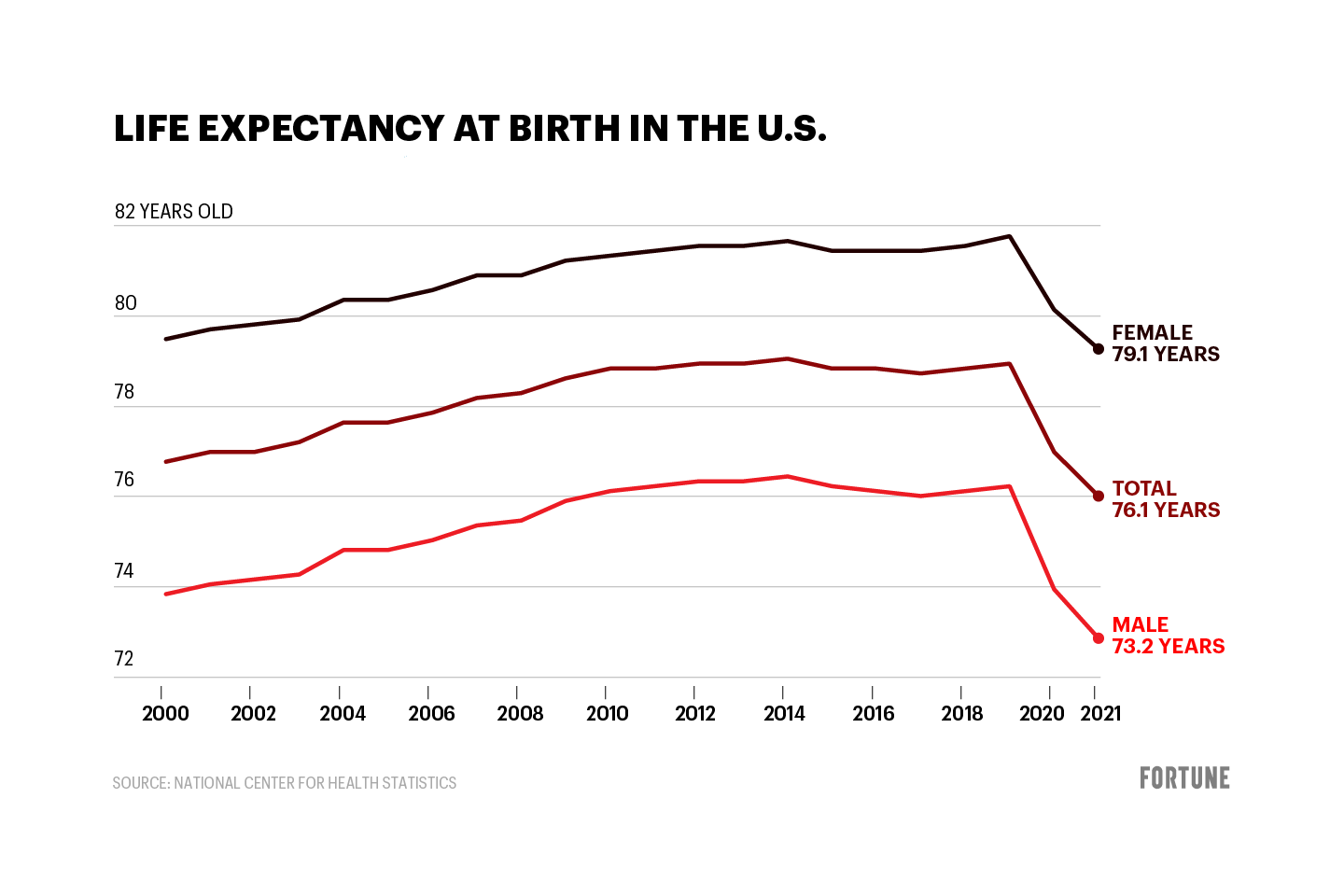
For the past few months, the US navy has been attacking drug-running boats from Venezuela. Videos show ships trying to run away with packages pushed overboard before the sailors are captured or killed. It’s claimed that the packages contained fentanyl, a deadly synthetic heroin. At the same time, there has been a dramatic drop in the rate of fentanyl deaths. Based on the graph above, it seems that some 1500 US lives were saved per month, from fentanyl death alone.
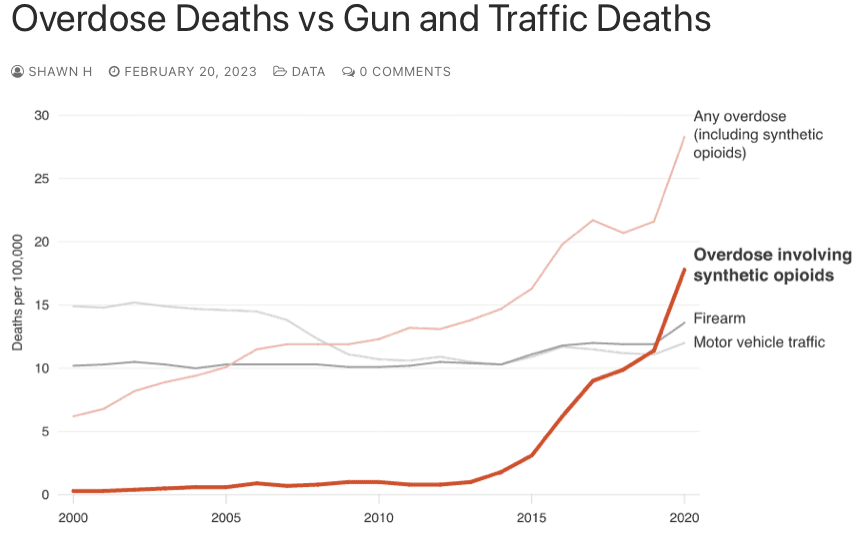
Opioid overdose deaths have exceeded gun or vehicle deaths since 2005. But there has been a big uptick since the introduction of synthetic opioids, about 2014. Fentanyl is now the leading cause of overdose deaths, alone outpacing gun and vehicle deaths, see graph.
It’s not clear that the attacks on the boats is a primary reason for the drop in deaths, by the way. A lot of credit goes to seizures at the Mexico and Canada border, including the decrease in migrant passage. Some of those were “mules”, carrying drugs. Improved screening at the border seems to have help stop the mules. In 2025, the DEA seized over 47 million fentanyl-laced pills and nearly 10,000 pounds of fentanyl powder, some made in the US, some brought in, cross-border.
An other positive change is increased screening of small packages, of value under $800. They previously entered the US, tariff free, at reduced postage rates. Chinese companies could send 2 oz packages to customers here for 70¢, cheaper than Americans could ship cross town. The DEA reports that most of the precursor chemicals enter the US in packages from China. More checking, and help from China, means fewer of these chemicals get in.
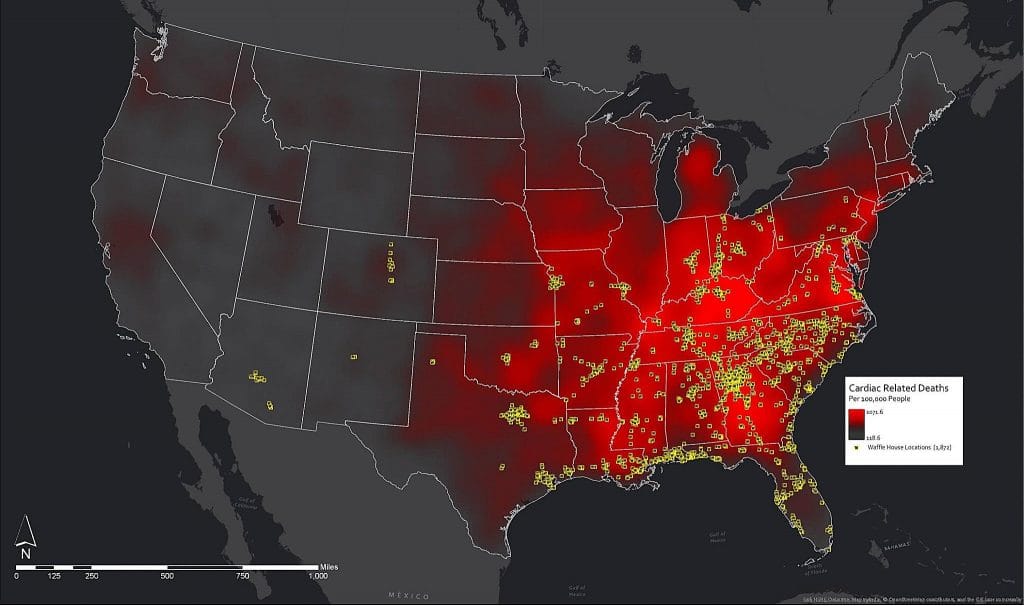
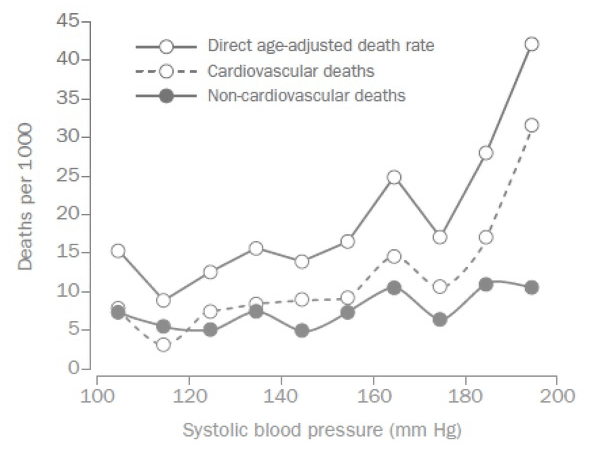
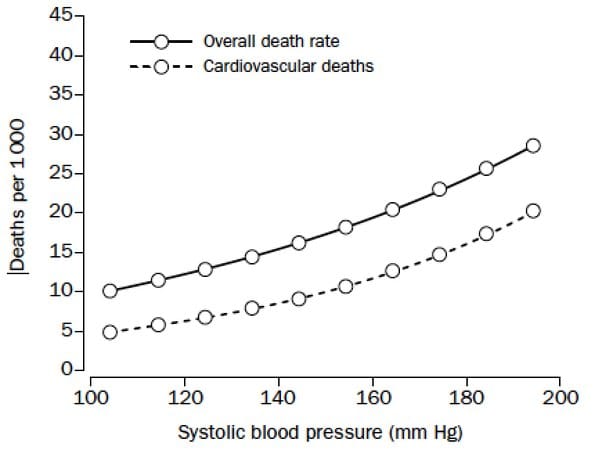
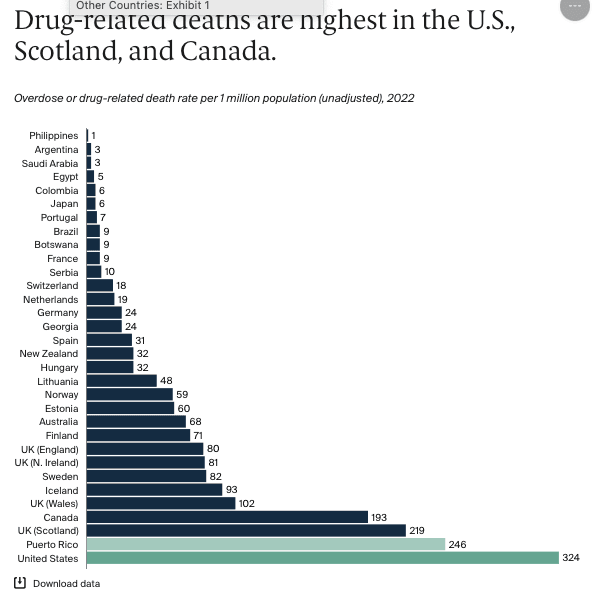
Before we compliment ourselves, our drug numbers are still vastly too high, about 70,000 overdose deaths in 2025, a vastly higher rate than in Europe or Japan, see chart below. The reason is, in my opinion, that we are over-diagnosed and over-medicated. We see ads for drugs on TV, magazines telling us to ask for a pill for any pain or discomfort. They’re all addictive. Doctors are happy to comply, and when the prescription stops, or stops being effective, you’re a hooked customer for heroin or fentanyl.
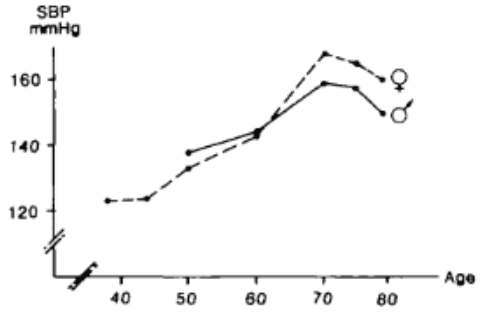
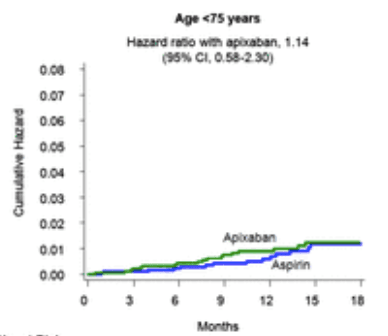
Addiction has become a middle-aged problem affecting mostly those 25 to 45. It’s made US lifespan significantly shorter. Doctors are curing the pain and killing us patients. Magazines, TV, and drug companies, too. Europe has stricter regulations on pills with fewer prescriptions allowed, no drug ads, and no automatic refills. Does everyone over 50 need blood pressure meds, for example.
Robert Buxbaum, January 26, 2026