I ran for water commissioner of Oakland county in 2016, a county with 1.3 million people and eight sewage treatment plants. One of these plants uses the rotating disk contractor, described previously, but the others process sewage by bubbling air through it in a large tank — the so-called, activated sludge process. A description is found here in Wikipedia, but with no math, and thus, far less satisfying than it could be. I thought I might describe this process relevant mathematics, for my understanding and those interested: what happens to your stuff after you flush the toilet or turn on the garbage disposal.
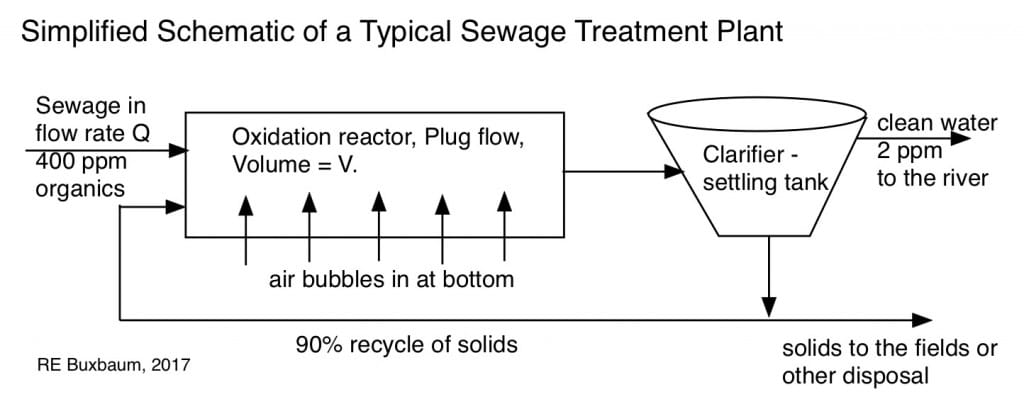
Simplified sewage plant: a bubbling, plug-flow bio-reactor with 90% solids recycle and a settler used to extract floc solids and bio-catalyst material.
In most of the USA, sanitary sewage, the stuff from your toilet, sink, etc. flows separately from storm water to a treatment plant. At the plant, the sewage is first screened (rough filtered) and given a quick settle to remove grit etc. then sent to a bubbling flow, plug-flow bioreactor like the one shown at right. Not all cities use this type of sludge processes, but virtually every plant I’ve seen does, and I’ve come to believe this is the main technology in use today.
The sewage flows by gravity, typically, a choice that provides reliability and saves on operating costs, but necessitates that the sewage plant is located at the lowest point in the town, typically on a river. The liquid effluent of the sewage, after bio-treatment is typically dumped in the river, a flow that is so great more than, during dry season, more than half the flow of several rivers is this liquid effluent of our plants – an interesting factoid. For pollution reasons, it is mandated that the liquid effluent leaves the plant with less than 2 ppm organics; that is, it leaves the plant purer than normal river water. After settling and screening, the incoming flow to the bio-reactor typically contains about 400 ppm of biomaterial (0.04%), half of it soluble, and half as suspended colloidal stuff (turd bits, vegetable matter, toilet paper, etc). Between the activated sludge bio-reactor and the settler following it manage to reduce this concentration to 2 ppm or less. Soluble organics, about 200 ppm, are removed by this cellular oxidation (metabolism), while the colloidal material, the other 200 ppm, is removed by adsorption on the sticky flocular material in the tank (the plug-flow tank is called an oxidation ditch, BTW). The sticky floc is a product of the cells. The rate of oxidation and of absorption processes are proportional to floc concentration, F and to organic concentration, C. Mathematically we can say that
dC/dt = -kFC
where C and F are the concentration of organic material and floc respectively; t is time, and k is a reaction constant. It’s not totally a constant, since it is proportional to oxygen concentration and somewhat temperature dependent, but I’ll consider it constant for now.
As shown in the figure above, the process relies on a high recycle of floc (solids) to increase the concentration of cells, and speed the process. Because of this high recycle, we can consider the floc concentration F to be a constant, independent of position along the reactor length.
The volume of the reactor-ditch, V, is fixed -it’s a concrete ditch — but the flow rate into the ditch, Q, is not fixed. Q is high in the morning when folks take showers, and low at night. It’s also higher — typically about twice as high — during rain storms, the result of leakage and illegal connections. For any flow rate, Q, there is a residence time for a bit of sewage flowing through a tank, τ = V/Q. We can now solve the above equation for the value of τ for an incoming concentration C° = 400 ppm, an outgoing concentration Co of 2 ppm. We integrate the equation above and find that:
ln (C°/Co) = kFτ
Where τ equals the residence time, τ = V/Q. Thus,
ln (C°/Co) = kFV/Q.
The required volume of reactor, V, is related to the flow rate, Q, as follows for typical feed and exit concentrations:
V = Q/kF ln( 400/2) = 5.3 Q/kF.
The volume is seen to be dependent on F. In Oakland county, tank volume V is chosen to be one or two times the maximum expected value of Q. To keep the output organic content to less than 2 ppm, F is maintained so that kF≥ 5.3 per day. Thus, in Oakland county, a 2 million gallon per day sewage plant is built with a 2-4 million gallon oxidation ditch. The extra space allows for growth of the populations and for heavy rains, and insures that most of the time, the effluent contains less than 2 ppm organics.

Bob Martin chief engineer the South Lyon, MI, Activated Sludge plant, 2016. His innovation was to control the air bubblers according to measurements of the oxygen content. The O2 sensor is at bottom; the controller is at right. When I was there, some bubblers were acting up.
As you may guess, the activated sludge process requires a lot of operator control, far more than the rotating disk contractor we described. There is a need for constant monitoring and tweaking. The operator deals with some of the variations in Q by adjusting the recycle amount, with other problems by adjusting the air flow, or through the use of retention tanks upstream or downstream of the reactor, or by adding components — sticky polymer, FeCl3, etc. Finally, in have rains, the settler-bottom fraction itself is adjusted (increased). Because of all the complexity. sewer treatment engineer is a high-pay, in demand, skilled trade. If you are interested, contact me or the county. You’ll do yourself and the county a service.
I’d mentioned that the effluent water goes to the rivers in Oakland county. In some counties it goes to the fields, a good idea, I think. As for the solids, in Oakland county, the solid floc is concentrated to a goo containing about 5% solids. (The goo is called unconsolidated sludge) It is shipped free to farmer fields, or sometimes concentrated to more than 5% (consolidated sludge), and provided with additional treatment, anaerobic digestion to improve the quality and extract some energy. If you’d like to start a company to do more with our solids, that would be very welcome. In Detroit the solids are burned, a very wasteful, energy-consuming process, IMHO. In Wisconsin, the consolidated sludge is dried, pelletized, and sold as a popular fertilizer, Milorganite.
Dr. Robert Buxbaum, August 1, 2017. A colleague of mine owned (owns?) a company that consulted on sewage-treatment and manufactured a popular belt-filter. The name of his company: Consolidated Sludge. Here are some sewer jokes and my campaign song.