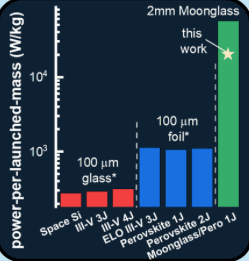
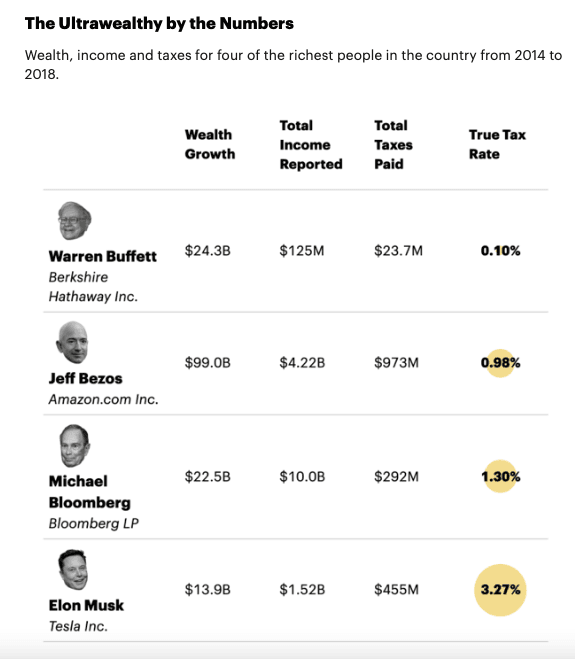
Jeff Bezos’s “Blue Alchemist” program recently got $25M from NASA to develop moon-based solar cell manufacturing on earth. See article here. The idea sort of makes sense to me: instead of transporting solar cells to the moon from earth, why not make them on the moon in bulk. Even light solar cells would weigh about 1kg/kW, making cells on the moon would reduce the effective weight per kW by a factor of 100 it is predicted, see figure. Given a need for megawatts of power, and the high cost to transport things to the moon, $1M/kg currently, this may make sense for the not super-distant future. Moon-made solar cells could reduce the cost per kW on the moon from $1million currently, to a mere $10,000/kW, cheap by moon prices, though super expensive by earth standards.
Elon Musk, perhaps out of envy or long-range vision, wants to go far further. He” recently’s posted’s proposed, at length a plan to launch moon-made solar cells into space along wit moon-made AI chips, with all this done to power AI centers in space, orbiting the earth or moon, see him discuss it here. He notes that “It’s always sunny in space”, so this electricity should be cheap. I don’t consider even moon-solar at $10,000/kW cheap, and power from these moon-launched cells will be pricer yet.
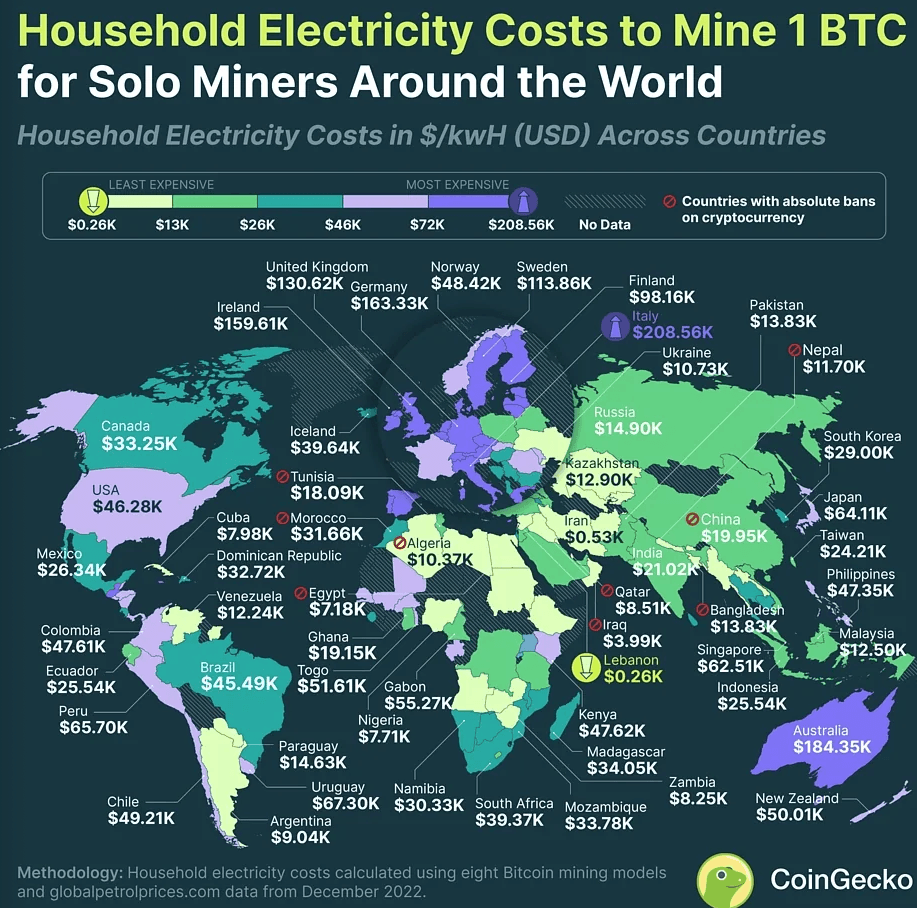
The reason all this makes sense to Musk is that he avoids the disruptions of solar power that come at night-time, and he avoids regulatory boards. He argues that there is no real alternative! given that power on earth is too hard and expensive, and complains that regulators oppose new power plants. I suspect there are some over-regulations, but some regulations are necessary, and I doubt he’ll avoid by going to space. As for the high cost of power, it’s really cheap in China, Lebanon, Iraq, Iran…Just look att he figure below showing the electric cost of bitcoin harvesting around the world. China runs on nuclear power or coal, delivering large-scale electricity at ~ 2¢/kWh. You can make power at a similar cost if you build your own plant, many of the bit-coin folks operate that way. It’s not exactly cheap, but a known technology, and cheaper than space solar amortized to less than 50 years.
AI chip-making is hard to do, even on earth, requiring water, chemicals, equipment and technical attention. Most companies can’t do it; China has barely cracked the technology. Doing it on the moon adds unnecessary difficulties: water and chemicals scarce, skilled servicing labor is hard to find. At some point, the moon and Mars community will want to make AI in space, but before that, they’ll want to make simpler things, like rice cookers. Until we have a fairly large community on the moon, why now make AI chips on earth. If he’s looking for practice, Musk could manufacture in a place that’s inhospitable, but more accessible than the moon: Greenland or Antarctica or the top of Everest. These locations are wam compared to the moon, and they have air and water, and I suspect electricity on Everest is cheaper than on the moon.
Operating AI centers in space is not particularly attractive, by the way. Chips have a tendency to flake-out in space because of cosmic radiation and stronger electromagnetic fields (EM). For this to work at all, chips have to be built specially robust, with correction software that must be particularly active, and you must shield everything from EM to a much greater extent than on earth.
I suspect the reason Musk wants to manufacture AI in space, and to operate there, is to over-shadow Bezos’s solar cell factory, and show off his own (Tesla) technology. Also to have a use for his Starships lifting heavy complicated things. It’s not a plan I would back.
Robert Buxbaum, March 1, 2026