As impressive as Lindberg’s transatlantic fight was in 1926, more impressive was George Schuster driving and winning the New York to Paris Automobile race beginning in the dead of winter, 1908, going the long way, through Russia. As of 1908, only nine cars had ever made the trip from Chicago to California, and none had done it in winter, but this race was to go beyond California, to Alaska and then over the ice through Russia and to Paris. Theodore Roosevelt was president, and Americans were up to any challenge. So, on February 12, 1908 there congregated in Times Square, New York, a single, US-made production car, along with five, specially made super-cars from Europe; one each from Italy and Germany; and three from France. The US car, a Thomas Flyer (white), is shown in the picture below. The ER Thomas company sent along George Schuster, as an afterthought: he was a mechanic and test-driver for the company, and was an ex bicycle racer. The main driver was supposed to be Montague Roberts, a dashing sportsmen, but the fellow dropped out in Cheyenne, Wyoming. Schuster reached the Eiffel tower on July 30, 1908, 169 days after leaving New York. The Germans and Italians followed. None of the French super-cars got further than Vladivostok, and one dropped out after less than 100 miles.
The race was sponsored by The New York Times and Le Matin, a Paris newspaper. They offered a large trophy, a cash prize of $1000, not enough to pay for the race, and the prospect of fame. The original plan was for drivers to go from New York to San Francisco, then to Seattle by ship, and Northern Alaska, driving to Russia across the Arctic ice. That plan was abandoned when Schuster, the first driver to reach Alaska, discovered ten foot snows outside of Valdez. The race was modified so that travel to Russia would be by ship. Schuster took his Thomas to Russia from Alaska, the other two drivers reached Russia from Seattle by way of Japan. Schuster was given a bonus of days to account for having taken the longer route. Because of his detour, he was the last to arrive in Russia. From Japan, the route was Vladivostok, Omsk, Moscow, St. Petersburg, Berlin, and Paris, 21,900 miles total; 13,341 miles driven. Schuster drove most of those 13,341 miles, protected by his own .32-caliber pistol, and mostly guided by the stars and a sextant. He’d taught himself celestial navigation as there were no roadmaps, and hardly any roads.

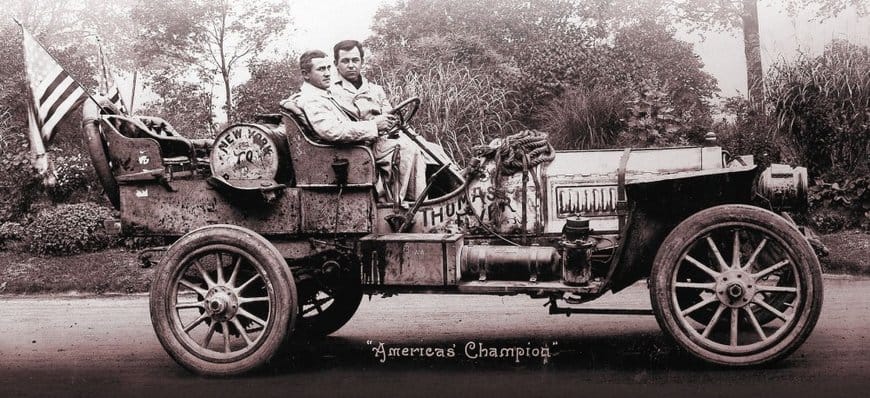
George Schuster driving the Thomas Flyer with another mechanic, George Miller, the Flyer was only American entry, and the only production motorcar in the race. Note that the flag has only 45 stars.
The ship crossing of the Pacific was a good idea given that, even in the dead of winter, global warming meant that the arctic could not be relied upon to be solid ice. As it was, Schuster had to content with crossing the Rockies in deep snow, and crossing Russia in the season of deepest mud. He reached the Eiffel tower at 6 p.m. on July 30, 1908. The German car had arrived in Paris three days ahead of Schuster, but was penalized to second place because the German team had avoided the trip to Alaska, and had traveled some 150 km of the Western US by railroad while Schuster had driven. The Italian team reached Paris months later, in September, 1908. That the win went to the only production car to compete is indicative, perhaps of the reliability that comes with mass production. That Mr. Schuster was not given the fame that Lindberg got may have to do with the small size of the prize, or with him being a mechanic while Lindberg was a “flyer”. Flyers were sexy; even the car was called a flyer. The Times saw fit to hardly mention Schuster at all, and when it did, it spelled his name wrong. Instead the Times headline read, “Thomas Flyer wins New York to Paris Race.” You’d think the car did it on its own, or that the driver was named Thomas Flyer.

Schuster in his Flyer crossing a swollen river in Manchuria.
The Times could not get enough of Montague Roberts; the driver of the first leg was famous and photographic. They tried to get Roberts to drive the last few miles into Paris, “once the roads were good”. And Roberts was the one chosen to drive in the hero-parade in New York, Schuster rode too, but didn’t drive. Schuster was feted by Theodore Roosevelt, though, who said he liked people “who did things.” Schuster said he’d never do a race like that again, and he never did race again.
The race did wonders for the reputation of American automobiles, and greatly spurred the desire for roads, but it did little or nothing for the E.R.Thomas company. Thomas cars were high cost, high power models, and they lost out in the marketplace to Henry Ford’s, low-cost Model T’s. You’d think that, in the years leading up to WWI, the US Army might buy a high cost, high reliability car, but they were not interested, and the Thomas company did little to capitalize on their success. The Flyer design that won the race was discontinued. It was a 60 hp, straight 4 cylinder engine version, replaced by lower cost Flyers with 3 cylinders and 24 hp. Shortly after that, Edwin R. Thomas, decided to drop the Flyer altogether. His company went bankrupt in 1912, and was bought by Empire Smelting. The original Flyer was sold in 1913 at a bankruptcy action, lot #1829, “Famous New York to Paris Racer.”
ER Thomas went on to found another car company, as was the style in those days. Thomas-Detroit went on make similar cars to the Flyer, but cheaper. The largest, the K-30, was only 30 hp. The original Thomas Flyer is now in the National Automobile Museum, Reno Nevada. after being identified by Schuster and restored. Here is a video showing the original Flyer being driven by a grandson of George Schuster. There is a lower-power Thomas Flyer (black) in a back space of the Henry Ford museum (Detroit). Protos vehicles, similar to the one that came in second, were produced for the German military through WWI. Their manufacturer, Siemens, benefited, as did the German driver.

Advertisement for the Protos Automobile, a product of Siemens motor company. The race did not include a production Protos but one made specially for the race.
The Thomas engine (and the Protos) engine) live on in a host of cars with water-cooled, four-cylinder, straight engines. In 1922, Chalmers-Detroit merged with Maxwell and continued to produce versions of the old Flyer design, now with an internal drive-shaft. The original Flyer was powered via a gear-chain, like a bicycle. In 1928, Maxwell was sold to Chrysler. Chrysler persists in calling their high-power, four-cylinder engines by the name Chalmers. As for Schuster, when ER Thomas closed its doors, he had still not been paid for his time as a race driver. He went to work for Pierce-Arrow, another maker of large, heavy vehicles. The “cheaper by the dozen” family (two parents, 12 kids) drove a Pierce-Arrow.
The Great race appears in two documentaries and two general audience movies, both comedies. The first of these was Mishaps of the New York–Paris Race, released by Georges Méliès, July 1908, just about as the Flyer was entering Paris. The second movie version “The Great Race” was released in 1965. It’s one of my favorite movies, with Jack Lemon as the Protos driver (called Dr. Fate in the movie), Tony Curtis as “The Great Leslie”, the Flyer driver. For the movie, the Flyer is called “The Leslie”, and with Natalie Wood as a female reporter who rides along and provides the love interest. In the actual race reporters from the New York Times, male, traveled in the Flyer’s rear seat sending stories back by carrier pigeon.

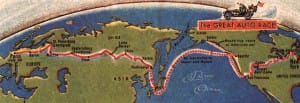
Path of the Great Race
As a bit of fame, here’s George Schuster in 1958 on “What’s my secret.” He was 85, and no one knew of him or the race. Ten years later, in 1968, Schuster finally received his $1000 prize, but still no fame. A blow-by-blow of the race can be found here, in Smithsonian magazine. There is also an article about the race in The New York Times, February 10, 2008. This article includes only two pictures, a lead picture showing one of the French cars, and another showing Jeff Mahl, the grandson of George Schuster, and a tiny bit of the flyer. Why did the New York Times choose these pictures? My guess is it’s the same reason that they reported as they did in 1908: The French car looked better than the Flyer, and Jeff Mahl looked better than George Schuster.
Robert Buxbaum, July 20, 2018. What does all this mean, I’ve wondered as I wrote this essay. There were so many threads, and so many details. After thinking a bit, my take is that the movie versions were right. It was all a comedy. Life becomes a comedy when the wrong person wins, or the wrong vehicle does. A simple mechanic working for a failing auto company beat great drivers and super cars, surpassing all sorts of obstacles that seem impossible to surpass. That’s comedy, It’s for this reason that Dante’s Divine Comedy is a comedy. When we see things like this we half-choose to disbelieve, and we half-choose to laugh, and because we don’t quite believe, very often we don’t reward the winner as happened to Schuster for the 60 years after the race. Roberts should have won, so we’ll half-pretend he did.
Like this:
Like Loading...