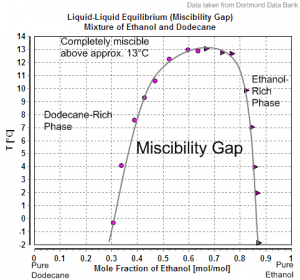
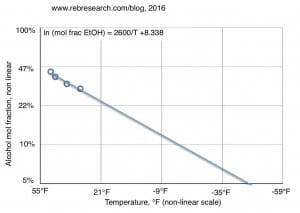
In a previous post, I made the case that one should avoid accepting loyalty requests as these are generally requests for your self-destruction. Someone who asks for loyalty is not saying he’ll provide you with good pay, a comfortable environment, empowerment, and good security. Rather that he wants your service despite little or not pay, discomfort, enslavement, and likely death or disgrace. There are some, few exceptions, but loyal service of this type rarely serves the servant.

Your chance of surviving as a minion is low; your chance as master is lower.
I’d now like to claim that having loyal followers hurts the leader, too, costing him good service, and separating him from health, friends, and family. Most leaders are better off as half of a duopoly, without minions, and only loose control of their workers. The first reason for this is to note that minions don’t do good work relative to free men. They die for no good reason (e.g. you forgot to feed them), or they stop work and wonder what you’d like next, or they get drunk and gripe, or they beat each other up over fervor or small territorial issues. They very rarely innovate or work together, and for any complex project like taking over the world (or the tristate area) needs workers who do. Good work requires pride in achievement, and a loyal slave has none.
Having loyal followers precludes one from having a close relationship with the followers (you can’t appear weak), and also with friends (your minions must have one leader, not two). The leader gets used to being surrounded by sycophants, and begins to doubt those who behave otherwise. The boss will begin to distrust friends and allies, those he needs to stay in power, as these are the very people who could most easily assist others to take leadership from him. Over time, the king, boss, monopolist and dictator share less and less. As a result they end up secret and bitter, with many fears and none he can call close. And what pleasure is there in power, if one can’t share the rewards with friends and family, or share the burden with others.

Only support someone who could rule reasonably honestly and well. Chaos is worse than a dictator. Kanin from the New Yorker.
A great number of kings have killed themselves in one way or another, very often because of overly large ambitions (see cartoon). King Saul, in the Bible is perhaps the first, Hitler is perhaps the most famous, and Colonel Qadhafi of Libya is perhaps the most recent. More often, maximum leaders are murdered, typically by friends and family. Famous examples include Julius Caesar, Augustus Caesar, and Nero; Charles I, Louis XVI, Richard III, and Tzar Alexander. Both the king of rock (Elvis) and the king of pop (Michael Jackson) killed themselves with drugs. Yet others died in needless wars or were exiled. Napoleon was defeated, exiled, returned, re-exiled and then murdered by an associate. It’s not that safe to be the infallible king. Perhaps the wisest move is that of Pope Benedict, who last year left Rome for a life of monk-like solitude. Machiavelli points out, in “The Prince”, that only two Roman Emperors died of natural causes, one because he became emperor at a very old age, and the other was Marcus Aurelius, an advanced ruler who empowered his subjects.

Political bosses and monopolist businessmen, though lower in power, don’t fare much better in life. Boss Tweed died in jail, as did Capone, Boss Pendergast. Even if they avoid jail, the fact that no one likes you takes a toll. No one liked Vanderbilt or Rockefeller, Carnegie, Morgan, or Fisk. While they lived, they could expect nothing more than senate investigations and ugly lampoons in the free press, plus an unfavorable memory after death. William Hearst and Howard Hughes died as virtual hermits, best remembered as the inspiration for “Citizen Kane” and “The Navigator.” Peter Cooper and Steve Jobs are different, industrialists liked in life and in death; and Bill Gates may join them too. Their secret was to empower others.

He’s being eaten alive by his power, money, and respect, as are all those he might love.
Woe to the wife, child or friend of the dictator. The wife and children of a king or king-pin rarely enjoy much of the power. The king-pin doesn’t trust them (often with good reason), and neither do the people. Stalin killed his wife and children as did Nero, Frederick the Great, Herod, Hitler, and quite a few others. It was said that is was preferable to be an animal in the courtyard of these greats than a son at their table. And even if the king or king-pin doesn’t kill his wife child or son, the people often do e.g. Marie Antoinette was killed shortly after Louis XVI and the Tzarina of Russia alongside Alexander III. Similarly, the wife of Hitler, the Mistress of Mussolini, and the wife of Nicolae Ceausescu all died at their husband’s side, sharing the punishment for their husband’s ambition.
The kings of Sparta fared relatively well, as did their wives, despite the militarism of Sparta. Their trick was that Sparta was a du-archy, a country with two kings. Sparta was strong and stable, and their kings (mostly) died at home. In business too, it seems the selfish leader should step back and become almost invisible. It helps him, and helps the people too. If the leader can’t share power this way, he or she should at least give people a simple choice between two things he controls and accepts (chocolate and vanilla; Democrat and Republican). Workers with a choice, even a small one, learn to act somewhat independently, and customers (or citizens) don’t complain as much either if they have some control over their fate. All will come to like the leader more, and the leader will like himself more. People stopped resenting Microsoft when there was a viable alternative, Apple, and Microsoft engineers benefitted by having a competitor to their products. I suspect that Bill Gates realized this would happen when he helped fund Apple’s return to the market. Unfortunately, most monopolists, bosses, and king-pins are too stupid, or too afraid to do this. In the end, it’s the trapped employee or follower who shoots the leader from behind.

The ideal situation is a delicate balance between control and freedom. A great leader will empower those around him and support the opposition. That was the unrealized sense of Mao Tse Tung’s hundred flowers movement (let 100 flowers bloom; left 100 schools of thought contend). It’s political tensegrity. Most leaders can not let go to do this (Mao could not). Still, there IS a sanity clause, Virginia. And a leader should know that there is no benefit to the king who gains the whole world and loses his friends, family and sleep.
Robert Buxbaum. Remember, remember the 5th of November; those oppressed, and those imagining themselves oppressed rise and plot.
Like this:
Like Loading...